
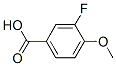
CAS: 403-20-3
3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid
3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid
Properties:
- Product Name: 3-Fluoro-4-methoxybenzoic acid
- Synonyms:274603: 3-fluoro-4-methoxybenzoate; RARECHEM AL BO 0870; TIMTEC-BB SBB006649; 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid
- CAS RN.: 403-20-3
- EINECS: Add
- Molecular Weight: 169.1304
- Molecular Formula: C8H6FO3
- Melting Point(℃): 209-213℃
- Boiling Point(℃): 286.4°C at 760 mmHg
- Flash Point(℃): 127°C
- Hazard Symbols: Xi Details
- Xi:
- Risk Codes: R36/37/38; Details
- R36/37/38;: Details
- Safety Description: S26;S37/39;Details
- S26;S37/39;: Details
FAQ:
What is 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid and what are its
uses?
3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid is a chemical compound that is commonly used as an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and dyes. It is known for its versatile applications in various industries due to its unique chemical properties.
How is 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid synthesized?
3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid can be synthesized through the reaction of fluorobenzene with potassium hydroxide and methanol. This process results in the formation of the desired product, which can then be purified and isolated for use in various applications.
What are the key properties of 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid?
3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid is a crystalline solid with a white or off-white color. It has a molecular formula of C8H7FO3 and a molecular weight of 168.14 g/mol. The compound has a melting point of around 131-135°C and is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and acetone.
What are the safety considerations when handling 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid?
As with any chemical compound, proper safety precautions should be taken when handling 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats. Additionally, the compound should be stored in a cool, dry place away from sources of ignition and incompatible materials.
What are the storage recommendations for 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid?
3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid should be stored in a well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources. The compound should be kept in a tightly sealed container to prevent moisture absorption and contamination. Proper labeling and segregation from other chemicals are also recommended to ensure safe storage practices.
3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid is a chemical compound that is commonly used as an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and dyes. It is known for its versatile applications in various industries due to its unique chemical properties.
How is 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid synthesized?
3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid can be synthesized through the reaction of fluorobenzene with potassium hydroxide and methanol. This process results in the formation of the desired product, which can then be purified and isolated for use in various applications.
What are the key properties of 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid?
3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid is a crystalline solid with a white or off-white color. It has a molecular formula of C8H7FO3 and a molecular weight of 168.14 g/mol. The compound has a melting point of around 131-135°C and is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and acetone.
What are the safety considerations when handling 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid?
As with any chemical compound, proper safety precautions should be taken when handling 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats. Additionally, the compound should be stored in a cool, dry place away from sources of ignition and incompatible materials.
What are the storage recommendations for 3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid?
3-fluorine-4-methoxybenzoic acid should be stored in a well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources. The compound should be kept in a tightly sealed container to prevent moisture absorption and contamination. Proper labeling and segregation from other chemicals are also recommended to ensure safe storage practices.

